Which Observations Correctly Describe the Second Law of Thermodynamics
1 3 4 5. Check all that apply.

Which Observations Correctly Describe The Second Law Of Thermodynamics Check All That Brainly In
Due to entropy which is the measure of disorder in a closed system all of the available energy will not be useful to the organism.
. At its heart is a property of thermodynamic systems called entropy. Check all that apply. The second law is also known as the Law of Increased Entropy.
The second law of thermodynamics can be expressed in several ways as below. Which of the following correctly states a limitation imposed by the first or second law of thermodynamics. Many processes have been developed which can convert work completely to heat.
Some useful energy is lost as heat whenever an energy transfer occurs. For example if we look at the piston in an engine the gas is heated to increase its pressure and drive a piston. 2nd law is based on the observation that whenever an energy transfer takes place a par.
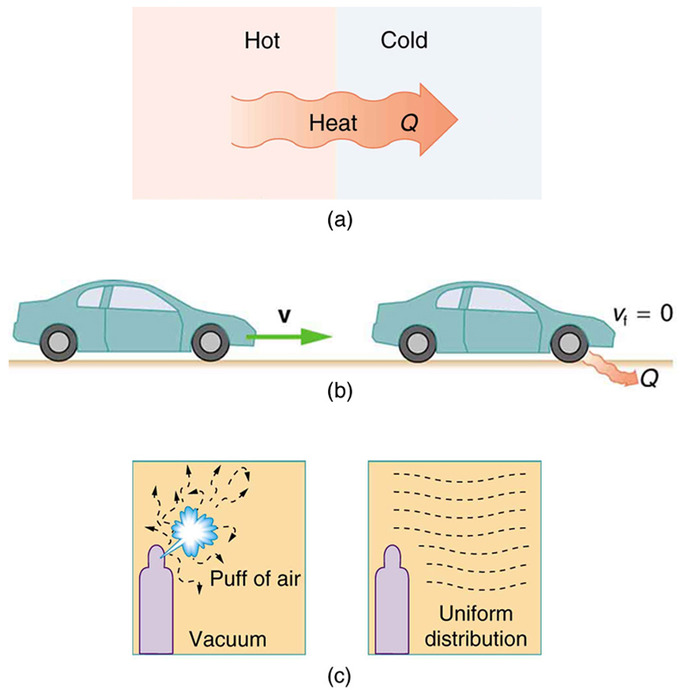
Thermal energy flows from a cooler object to a warmer object. Thermal energy that is not used to do work is often released to the surroundings. Which best describes the second law of thermodynamics.
Many approaches have been tried that include the statistics and thermodynamics heat temperature and work done. The first law describes the direction of thermal energy but. The first law describes how thermal energy is conserved but not the direction it moves.
This increase in entropy is due to the energy possessed by the matter particles which has resulted in their motion or movement. Thermal energy flows from a warmer object to a cooler object. 1Not all the thermal energy in a thermal system is available to do work.
Start studying Second Law of Thermodynamics-Assignment. The second law states that there exists a useful state variable called entropy S. Thermal energy that is not used to do work is often released to the surroundings.
The second law can be expressed in several ways the simplest being that heat will naturally flow from a hotter to a colder body. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that when energy is transferred there will be less energy available at the end of the transfer process than at the beginning.
When the energy of the system increases matter moves more freely and change in entropy that is disorderliness of the system increases. Irreversible processes involve dissipative factors which reduces the. 128116 The second law clearly explains that it is impossible to convert heat energy to mechanical energy with 100 per cent efficiency.
This implies that a heat engine or a refrigerator with 100 energy efficiency cannot be constructed. Due to entropy which is the measure of disorder in a closed system all of the available energy will not be useful to the organism. When is negative a process will proceed spontaneously and is referred to as exergonic.
The correct option is. Thermal energy flows from a cooler object to a warmer object. Entropy and Evolution Why are young-earth creationists so excited about thermodynamics.
Delta S delta Q T For a given physical process the combined entropy of the system and the environment remains a constant if the process can be reversed. Consider the growth of a farmers crop over a season. Entropy increases as energy is transferred.
The second law may be formulated by the observation that the entropy of isolated systems left to spontaneous evolution cannot decrease as they always arrive at a state of thermodynamic equilibrium where the entropy is highest at the given internal energy. The spontaneity of a process can depend on the temperature. The first law describes how thermal energy is created but not how it can be destroyed.
These facts are expressions of the Second Law of Thermodynamics. The entropy of the universe must decrease to account for the increased entropy associated with plant growth. The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that when energy is transferred there will be less energy available at the end of the transfer process than at the beginning.
Which best describes how the first and second laws of thermodynamics are related. The second law of thermodynamics indicates that a Carnot engine operating between two given temperatures has the greatest possible efficiency of any heat engine operating between these two temperatures. In 1976 Henry Morris explains his great discovery.
Which observations correctly describe the second law of thermodynamics. The most devastating and conclusive argument against evolution is the entropy principleThis principle also known as the Second Law of Thermodynamics implies that in the present order of things evolution in the vertical sense. Check all that apply.
The second law of thermodynamics says that the entropy of the universe always increases for a spontaneous process. It is impossible to convert heat completely into work without some other change taking place. According to second law of thermodynamics.
2Thermal systems spontaneously change only in certain ways and in partic- ular spontaneous heat flow always goes from a body at higher temperature to a body at lower temperature. Which observations correctly describe the second law of thermodynamics. The process of photosynthesis produces energy that the plant uses to.
Up to 256 cash back Which best describes the first law of thermodynamics as compared to the second law of thermodynamics. At constant temperature and pressure the change in Gibbs free energy is defined as. 6 rows Observation 2.
Which observations correctly describe the second law of thermodynamics. The second law is based on experimental observations and the atomistic understanding of the processes remain elusive among high school and university students. View the full answer.
Thermal energy flows from a warmer object to a cooler object. It is impossible to build a perfect heat engine or a perfect refrigerator. The change in entropy delta S is equal to the heat transfer delta Q divided by the temperature T.

Chapter 5 The Second Law Of Thermodynamics Updated 7 5 2014

No comments for "Which Observations Correctly Describe the Second Law of Thermodynamics"
Post a Comment